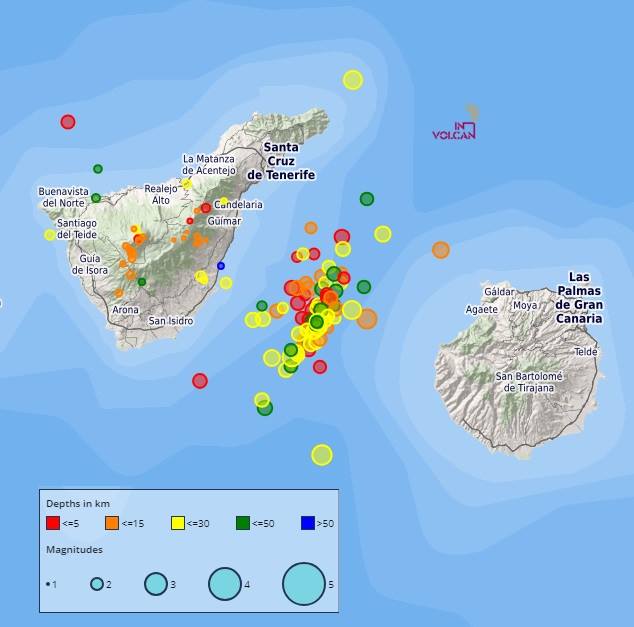
Involcan ha detectado ya unos 200 pequeños terremotos en la zona donde se concentra normalmente la mayor parte de la sismicidad registrada en Canarias
Sismicidad localizada por la Red Sísmica Canaria durante los últimos 30 días. / INVOLCAN
La Red Sísmica Canaria (INVOLCAN) ha informado hoy a través de su perfil en Facebook de que continúa el enjambre sísmico que comenzó en la tarde del pasado día 29 de abril a las 16.00 horas UTC y que se localiza entre las islas de Tenerife y Gran Canaria.
Recent developments on the world political stage have brought the destructive potential of electromagnetic pulses (EMP) to the fore, and people seem to have internalized the threat posed by a singl…

hackaday.com
ANTENAS GWEN UNA DE TANTAS
Reliability Through Physics
GWEN began as a patch for a perceived gap in the communications network connecting the country’s strategic nuclear assets — primarily the launch control centers (LCC) of the ballistic missile launch facilities — to the National Command Authority, which is basically the president. Like all strategic communications systems, GWEN was designed to incorporate best practices for surviving the electromagnetic effects of an EMP. But GWEN had another mission.
G
round wave propagation. Source:
Electronics Notes
Groundwave propagation is the tendency of certain radio waves to hug the surface and amow the curvature of the earth and is an exception to the general rule that radio waves only travel in straight lines. The earth acts as a conductor below 5 MHz, so radio waves traveling along the surface of the earth induce currents. The induced currents slow down propagation near the surface, curving the wavefront down as it spreads out. There is considerable attenuation of the signal, of course, and careful consideration has to be given to antenna design and construction. But when properly engineered, ground wave propagation systems can be very effective at over-the-horizon communications that do not rely on the ionosphere.
Groundwave propagation requires long wavelengths to work, so GWEN operated in the low frequency (LF) band from 150 to 175 kHz, well below the commercial AM radio medium frequency (MF) band from 530 to 1700 kHz.
GWEN Nodes
A GWEN relay node. Source:
Wikipedia, public domain.

GWEN was envisioned as a wide area network of LF
relay nodes about 150 to 200 miles apart. Each GWEN relay node communicated to
input-output nodes, which were generally located at Air Force bases and other such facilities. The relay nodes were to take command and control messages from the IO nodes and propagate them over the entire network until they reached
receive-only nodes, typically the LCC bases. GWEN encoded messages on the LF signals using minimum-shift keying at a data rate of 1200 bps. Messages were encrypted, of course.
Only about 58 of the planned 240 GWEN stations were built between 1982